COPD
Still Searching for COPD specialist ? Don't worry Learn about COPD in detailed and get educated!
What is a COPD?
COPD, or Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, is a lung condition that makes it hard to breathe. It usually happens because of smoking or long-term exposure to irritants like air pollution or chemicals. With COPD, your airways become narrower and it’s harder for air to flow in and out of your lungs.
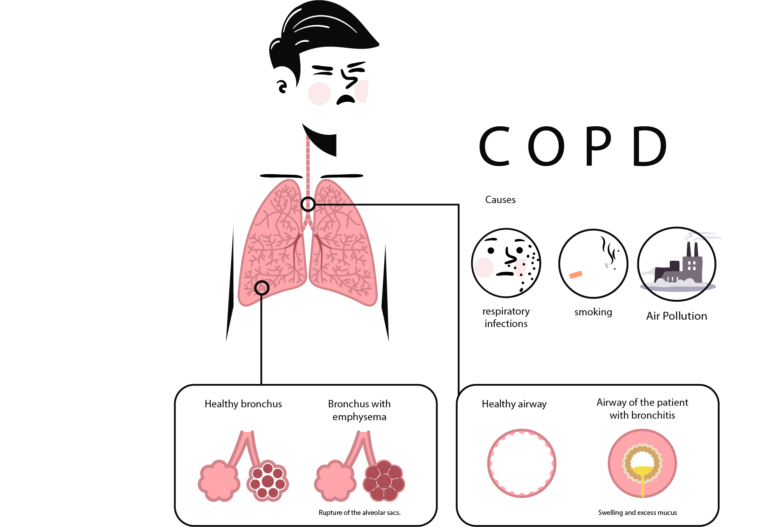
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) encompasses chronic bronchitis and emphysema, two prevalent lung conditions.
What is Chronic Bronchitis?
Chronic bronchitis is a type of COPD characterized by inflammation of the bronchial tubes, leading to a persistent cough with mucus production for at least three months in two consecutive years.
What is Emphysema?
Emphysema is a type of COPD characterized by damage to the air sacs in the lungs, leading to difficulty in exhaling air and causing shortness of breath and reduced lung function over time.
Symptoms of COPD, which includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema, often manifest as persistent coughing, wheezing, and breathlessness, especially during physical activities.
Chronic bronchitis is characterized by a chronic cough with sputum production, whereas emphysema involves the destruction of the air sacs in the lungs, leading to difficulty in exhaling air.
Additionally, individuals with COPD may experience chest tightness and frequent respiratory infections. These symptoms can vary in severity and tend to worsen over time, impacting daily life and overall well-being.
The primary cause is cigarette smoking, but long-term exposure to other lung irritants like secondhand smoke, air pollution, chemical fumes, and dust can also contribute.
Smoking damages the airways and air sacs in the lungs, leading to inflammation and narrowing of the air passages. Over time, this damage becomes irreversible and results in the symptoms characteristic of COPD.
Regularly take a lung test with your physician or get a consultation with our COPD Specialist Today.
Preventing COPD mainly involves avoiding smoking and minimizing exposure to lung irritants. Quitting smoking, with guidance from a COPD specialist if needed, is the single most effective way to reduce the risk of developing COPD or slowing its progression.
It’s also essential to stay away from environments with high levels of air pollution or harmful chemicals. Using protective equipment in workplaces with exposure to dust or fumes can also help prevent lung damage.
COPD treatment involves consulting a COPD specialist for personalized care. Medications like bronchodilators and corticosteroids are commonly prescribed to ease symptoms and reduce inflammation in the airways.
Pulmonary rehabilitation programs offer exercise training and education to improve lung function and quality of life. In severe cases, oxygen therapy or surgical interventions may be necessary.
Regular monitoring and adherence to treatment plans are essential for effectively managing COPD and minimizing its impact on daily life.
Frequently Asked Questions
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, and asthma are both chronic lung conditions affecting airflow. While asthma is characterized by reversible airway inflammation, COPD involves irreversible damage to the airways and lungs, leading to breathing difficulties.
- Yes, although smoking is the primary cause of COPD, non-smokers can also experience similar breathing problems due to exposure to pollutants like secondhand smoke, air pollution, or occupational hazards.
- Early signs may include chronic cough, shortness of breath, wheezing, chest tightness, and frequent respiratory infections.
- No, it is not reversible or curable. However, treatments can help manage symptoms, slow down disease progression, and improve quality of life.
moking damages the airways and lungs, leading to inflammation and narrowing of the air passages. This damage, along with exposure to other lung irritants, can result in breathing difficulties similar to COPD.
- Some natural remedies, such as breathing exercises or certain herbal supplements, may provide symptomatic relief. However, they should not replace medical treatments, and consulting with a copd specialist is essential.
- Yes, exposure to pollutants like air pollution, secondhand smoke, or workplace chemicals can exacerbate breathing difficulties and lead to respiratory flare-ups.
- Regular exercise can help improve cardiovascular health, strengthen respiratory muscles, and increase endurance, which may alleviate breathing difficulties and enhance overall well-being.
- Yes, it’s crucial for individuals with breathing difficulties to receive the flu vaccine annually to prevent flu-related illnesses, which can exacerbate respiratory symptoms.
- A healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support overall health and may help manage breathing difficulties. Staying hydrated and maintaining a healthy weight are also important.
- Chronic bronchitis is characterized by inflammation of the bronchial tubes, leading to a persistent cough with mucus production. Emphysema, on the other hand, involves damage to the air sacs in the lungs, causing difficulty in exhaling air.
- Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider, including consultations with a COPD specialist, are essential for monitoring disease progression, adjusting treatment plans, and addressing any new or worsening symptoms.